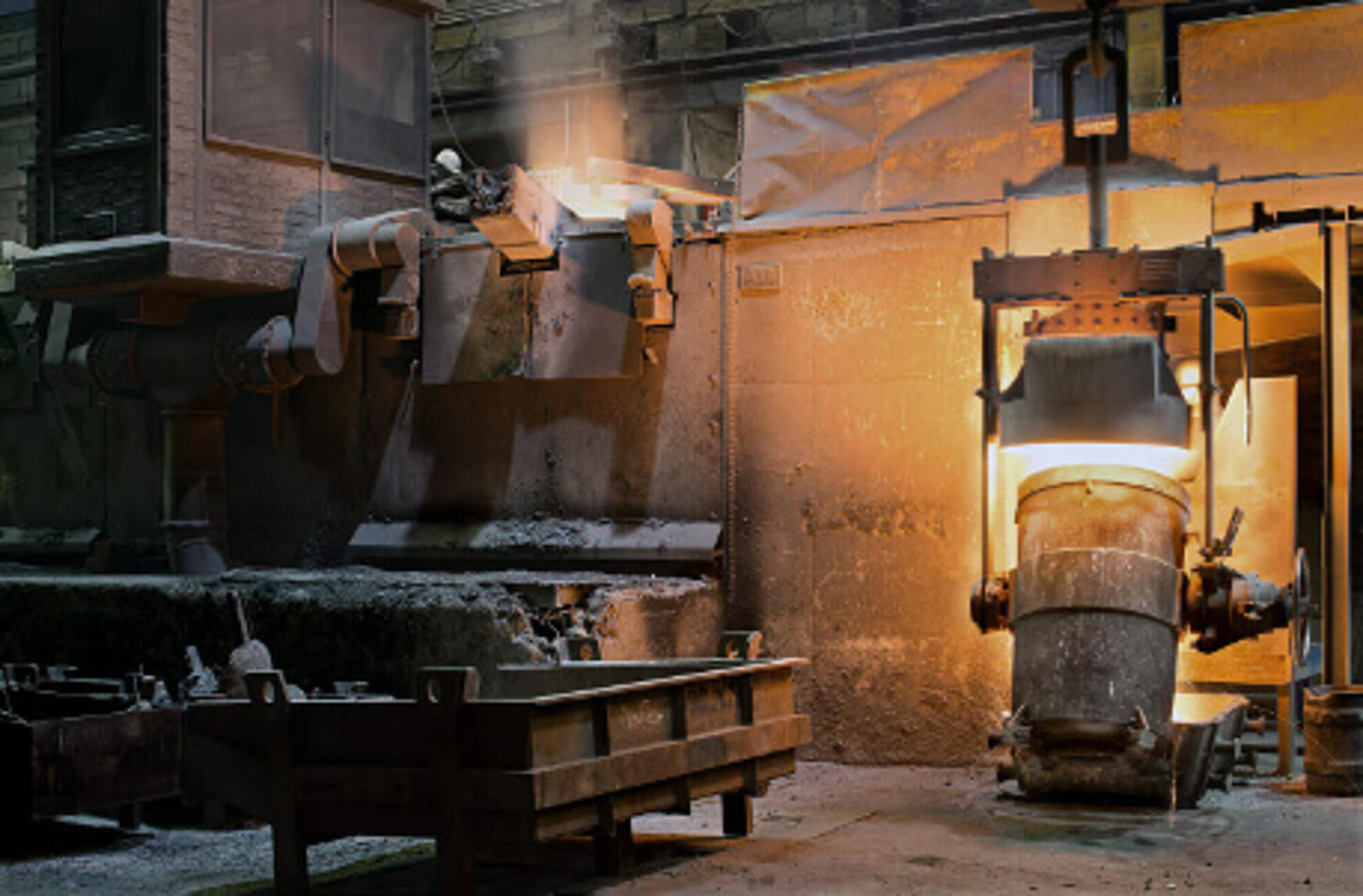
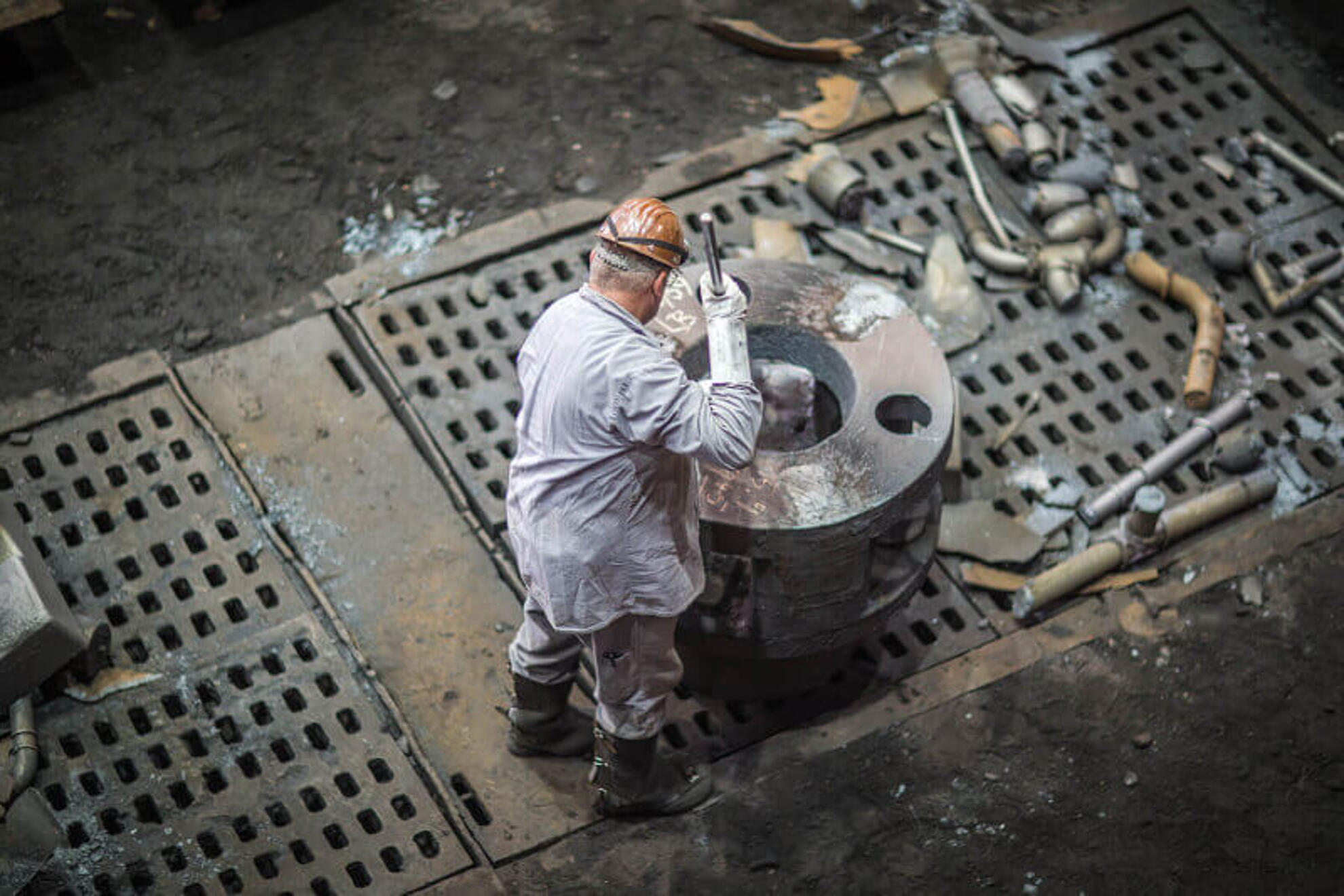
Wind power technology in the Silbitz Group
The expansion of wind power technology is one of the most important components of the global plans to continuously reduce the use of fossil fuels and hazardous nuclear power. At the beginning of the development in wind power technology, the wind turbines were still relatively small compared to today’s standard, had smaller rotor blade diameters and therefore a much lower energy yield. Thus, the energy mix in the past was very low. Through continuous development and defined plans to increase the share of wind power technology in power generation, more powerful, larger and more technically sophisticated wind turbines and components have been developed and brought to series production. Due to further developments and plans in wind power engineering, even higher demands will be placed on the material of the towers, the rotor blades, the gearbox and, above all, on the components of the wind power plants themselves. In the field of wind power technology, the Silbitz Group manufactures ready-to-install cast parts for wind turbines, according to your specifications and requirements, including heavy-duty and complex components made of a wide variety of materials.
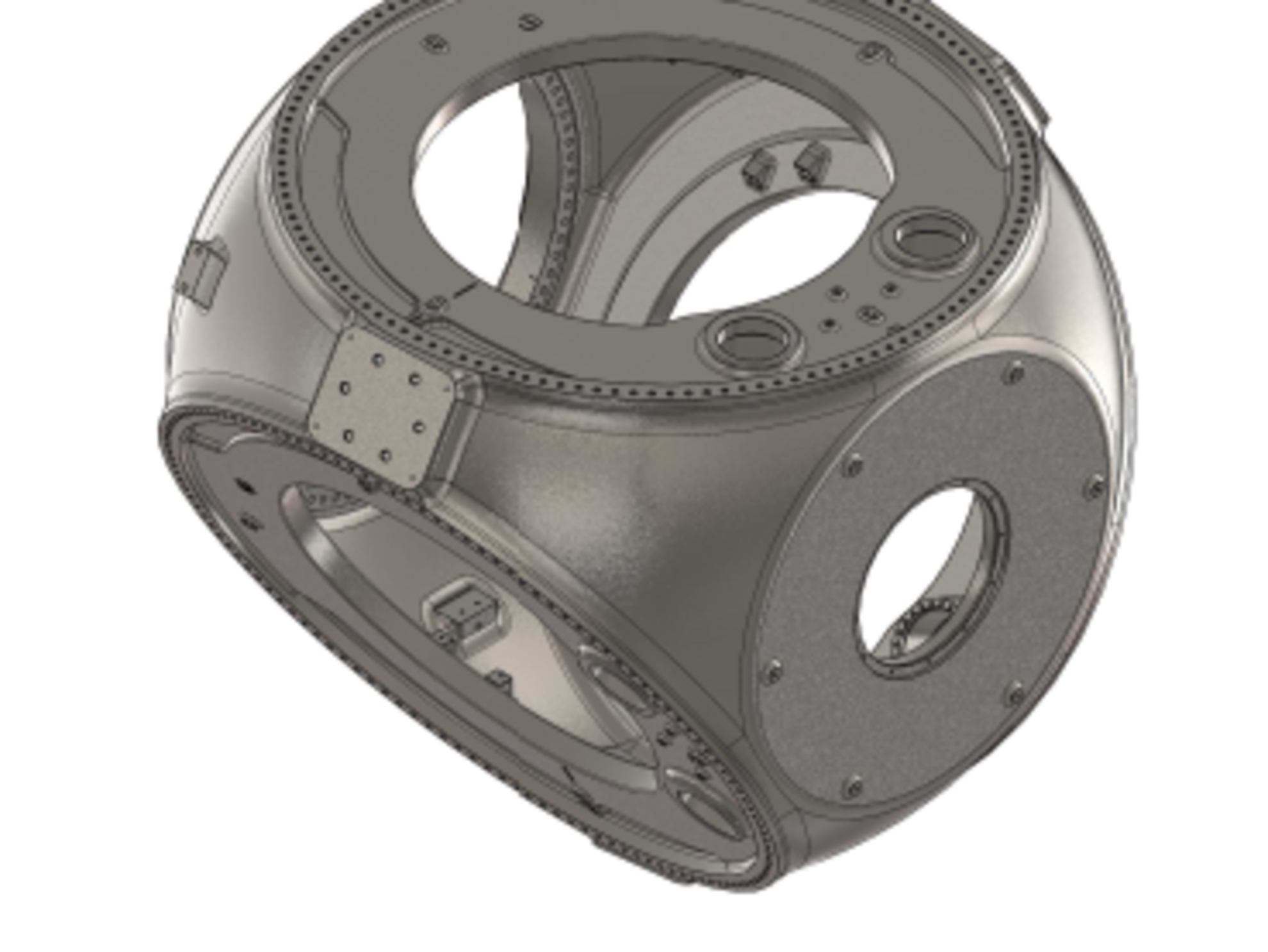
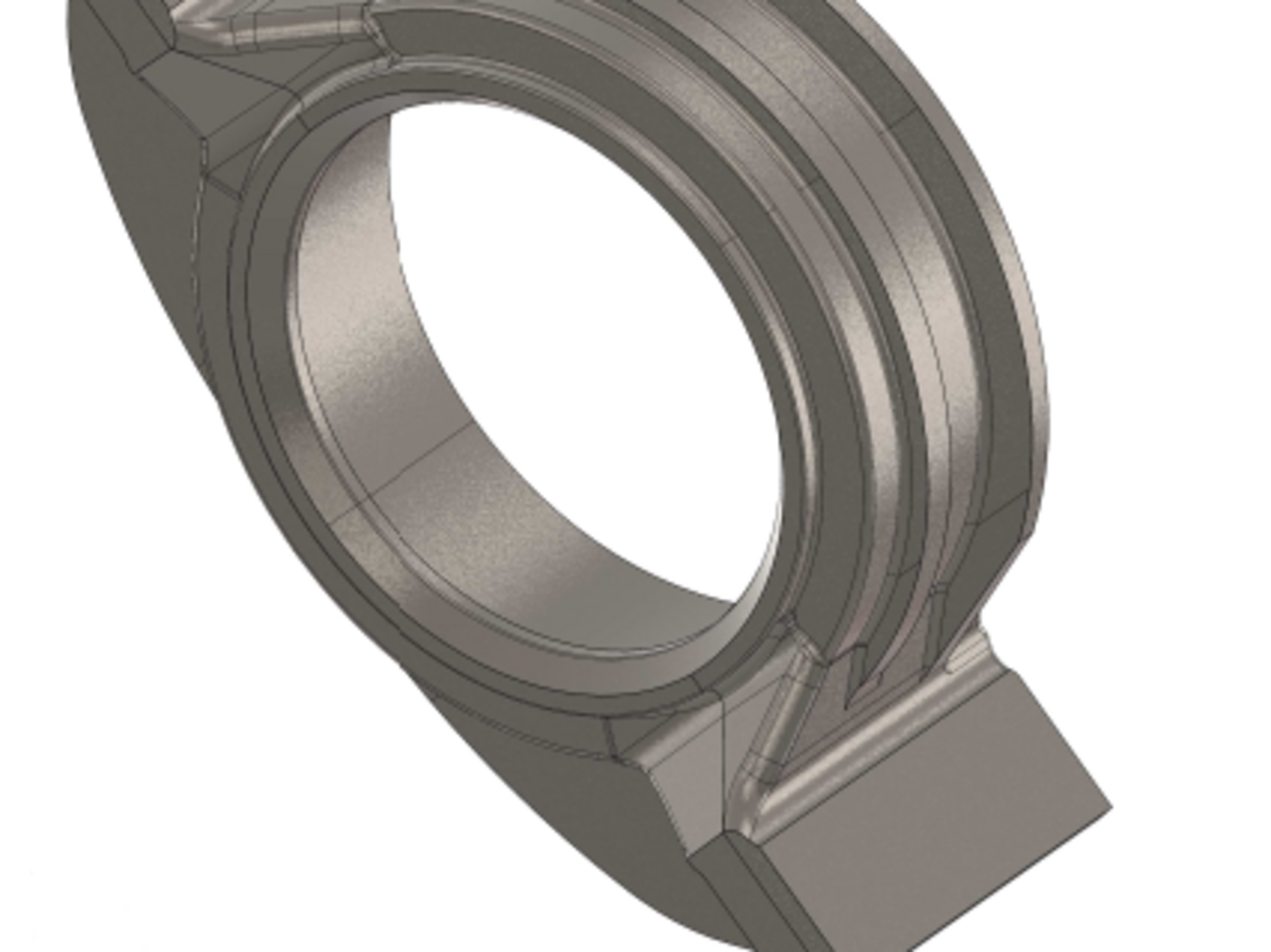
Examples for complex wind turbine components:
- Planetary bar and housing
- Castings for the turbine plant
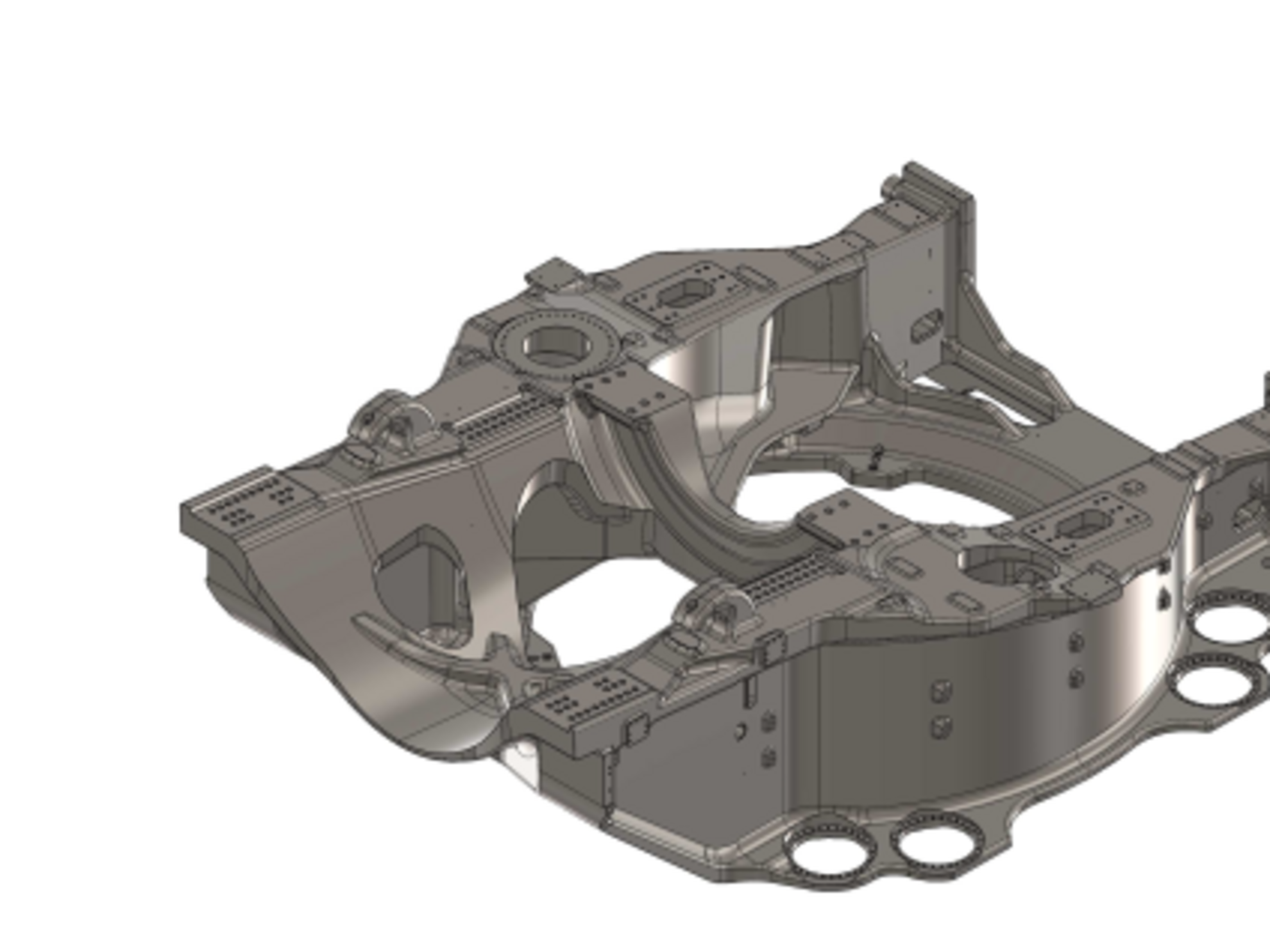
- Rotor hub and machine carrier or base frame
- Numerous other applications ranging from 20 kg to 45 tons
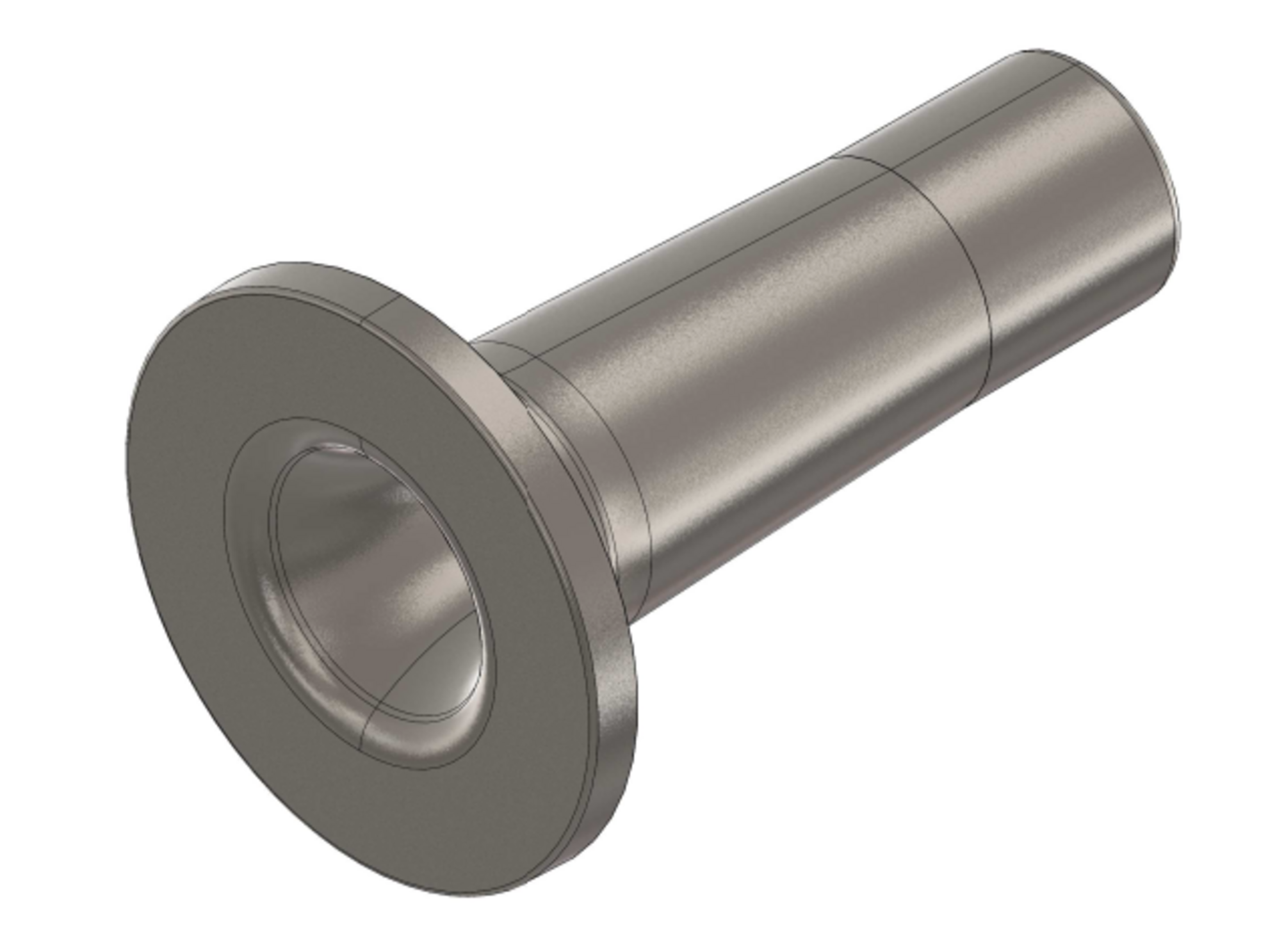
Individual components for wind power technology
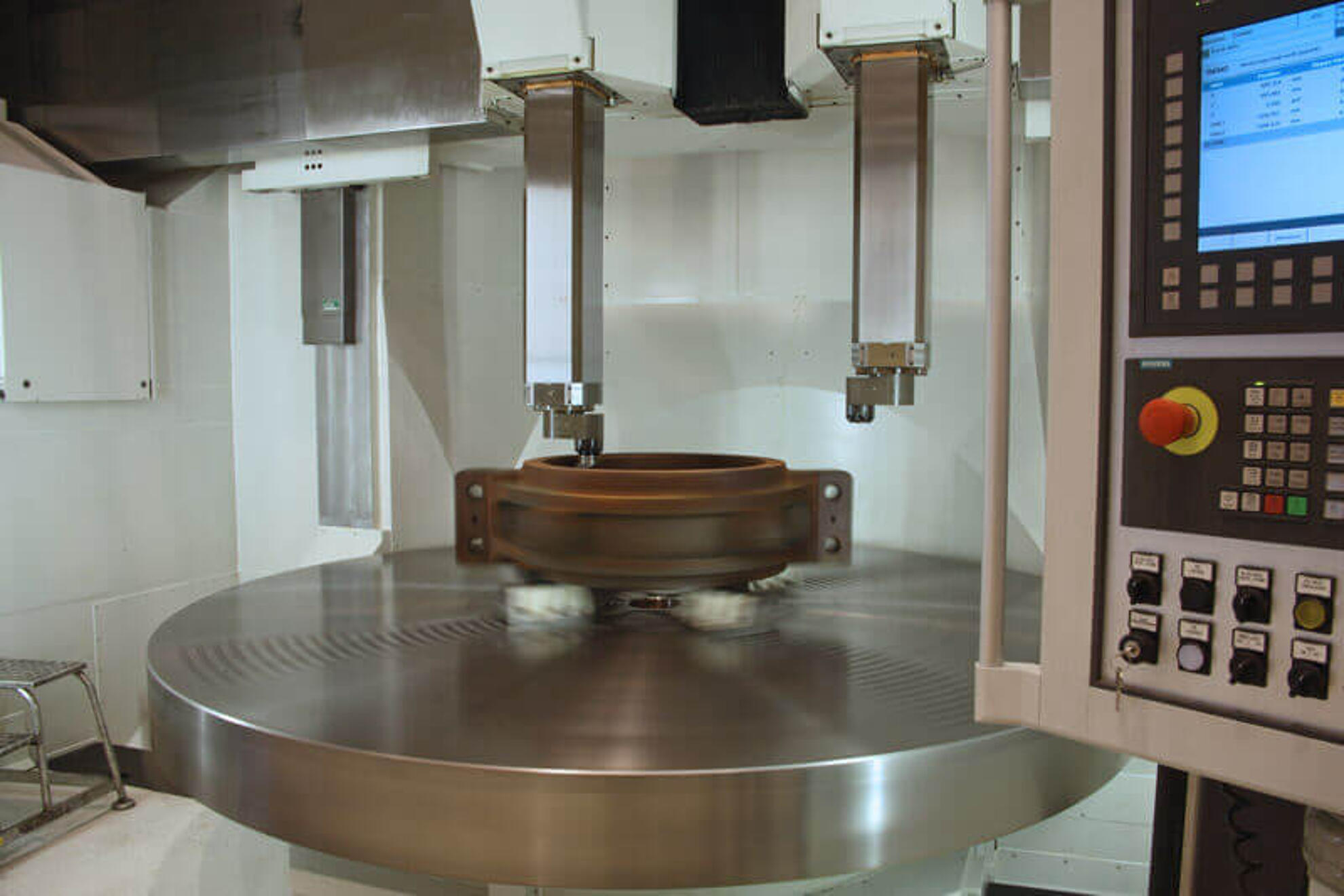
The Silbitz Group manufactures bearing housings, coupling housings, gearbox housings, main rotor shafts, rotor hubs and machine carriers with a respective unit weight of 0.5 to 45 tons in the area of wind power technology. The material of individual components consists, for example, of EN-GJS-400-18LT, a spheroidal graphite cast iron and of EN-GJS-500-14, a mixed-crystal-strengthened material. Upon delivery, all components for wind power technology can be mechanically processed and also provided with a high-quality coating.
Wind power technology is the future
According to the publications of the Federal Association for Wind Energy, the hub height of the largest wind turbines increased from 40 meters by 3.8 times to up to 152 meters within the years 1985 and 2015. The diameters of the rotor blades have grown by 6.5 times. Meanwhile, they have a diameter of about 160 meters. These large wind turbines generate extremely high forces and loads, which must be carefully considered in the design of this modern wind power technology, especially for the safety of humans and animals. While in 1985, the largest wind turbines, with a rotor diameter of 20 meters, produced 95 megawatt hours of power at an output of 80 kilowatts, inh 2015 it was already 15,000 megawatt hours at 7,000 kilowatts.